The first thing that comes to mind when you think of a portable music player is walking down the road listening to your favourite tracks with your headphones on. Whilst you might connect your headphones to a DAC, headphone amplifier or HiFi system at home, when you’re out and about, the most common solution is to use your smartphone as an audio player. However, the more demanding amongst you might not be satisfied with this solution, preferring instead to use devices tailored for the listening experience. After all, a smartphone is for making calls. If you want to listen to great quality music outside the house, you need a portable music player. A modern take on the Walkman, there are a myriad of models available to suit all budgets. Follow our advice to pick the right one for you.
Portable Music Players
Forty years ago, a battery-operated cassette player accompanied by simple headphones was introduced to the public: the Walkman. Today, this cassette player has all but disappeared, though there are those who wish to revive it. There’s no doubt about it though; music is much easier to move around on a memory card that can hold thousands of tracks. Not to mention that the difference in sound quality between the limited abilities of magnetic tape and the limitless resolution of FLAC or DSD files is frankly immeasurable.
The portable music player no longer has any moving mechanical parts. Its primary function is to read digital music, convert it to analogue and send it to the headphone output. There’s nothing exceptional about these functions anymore, with them being easily accessible even to models costing as little as £25. However, more sophisticated music players differ from these entry-level devices in three respects:
- Their playback capabilities offer the best possible resolutions, thanks to the high-quality processing of music files
- Their storage capacity is large enough for your entire personal library
- They feature power outputs to correctly power all kinds of headphones
The smartphone may appear to be a good alternative to the digital music player since it offers the same functions, just without the headphone socket (though it’s hard to imagine high-quality headphone listening without wired headphones). Plus, smartphones also offer similar storage capabilities, especially if they have an integrated SD card reader. However, when it comes to audio processing, there’s no contest. No smartphone is specifically designed to produce the highest quality sound possible. There’s no high-end digital-to-analogue converter, let alone dedicated end-to-end audio stream processing. Smartphones are not music players: these are two very different devices.

Advanced Audio Processing and Quality Conversion
Many portable music players contain components that meet a certain level of quality. This applies primarily to the converter (DAC). The best portable music players have chips identical to those found in home HiFi equipment: a key thing to consider when selecting a player that will provide the best sound experience. Other components in the audio signal path are also important, with manufacturers of the most advanced portable music players often using components from the best suppliers. Some select unexpected solutions (such as mini-tubes or FPGA chips) to ensure signal integrity, whilst others multiply the number of conversion chips. A DSP type processor means the user can adapt the sound to their taste by altering the equalisation or playing around with ambience settings. All these elements also guarantee a wide range of compatibility for audio file playback. Hi-Res is often taken for granted, but it covers most samplings and specific formats, such as MQA and DSD.
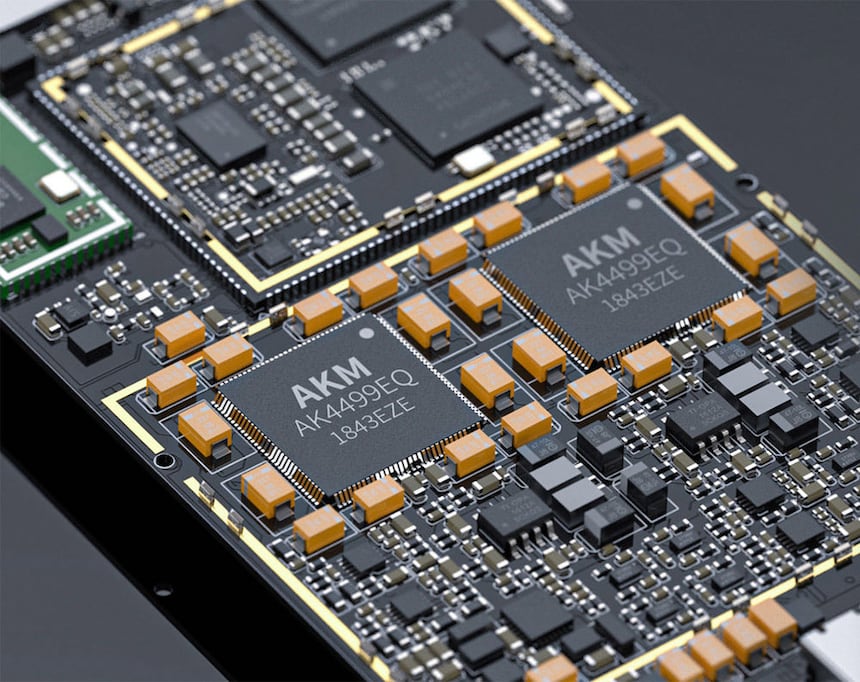
Extensive Storage for your Entire Music Library
Almost every portable music player has hundreds of megabytes of internal storage space. With 256 or 512 MB, you can take thousands of CD-quality tracks with you wherever you go (by thousands, we mean about 15,000 if you have 512 MB of storage). However, you might find this capacity isn’t enough if you’ve got a lot of high-resolution files. Some portable music players are equipped with an SD card slot, sometimes two. Depending on the model (which you should check before buying), 1 or 2 TB cards might be accepted. This multiplies the player’s capacity so you can take your entire music library with you everywhere. You can always keep multiple SD cards in your pocket, too—perfect for anyone with a perpetually expanding music collection.

The Right Power Output for Your Headphones
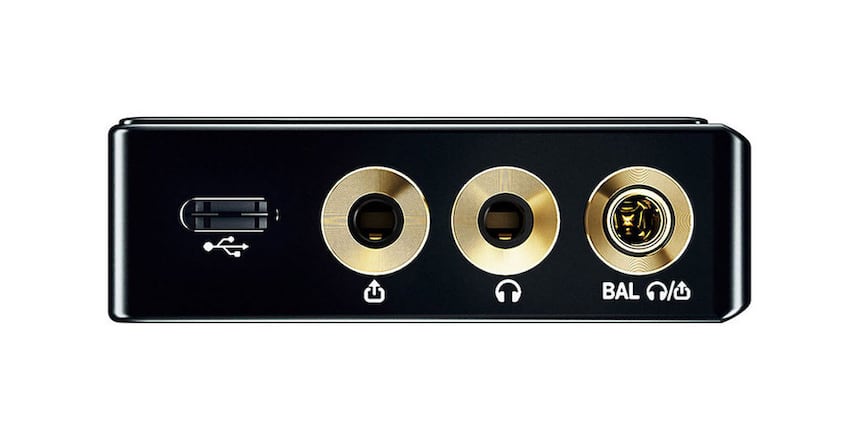
A key function of a portable music player is to optimally power wired headphones; a tricky task considering the range of headphones on offer is broad, with very different characteristics from one model to another. Impedance is arguably the most important of these characteristics: the higher the impedance, the more power the player will need to deliver. You should check the available power (expressed in mW) to ensure the combination is effective. Another essential feature is connection. There are several socket formats for headphones, three of which tend to be used on portable music players, all of them mini-jack: 2.5 mm, 3.5 mm and 4.4 mm. The 3.5 mm socket is the most common, corresponding to a classic unbalanced stereo connection. The two other sockets are balanced, with the left and right channels completely isolated from each other to achieve better sound quality. It’s essential to check beforehand whether the portable music player you’re interested in is equipped with the right socket for your headphones.

Which Portable Music Player Should You Choose?
We’ve looked at the three key criteria to consider when choosing a portable music player: audio processing, storage and headphone output. These are essential as selecting the wrong option can quickly make your new device incompatible with your needs, depending on your expectations and the type of headphones you own. Naturally, budget also plays a role in your decision, but there are other factors that might also guide your choice.
Interface
The vast majority of portable music players use Android for their touchscreen interface, making navigation similar to that of a smartphone: icon-based menu at the bottom of the screen, access to settings by sliding your finger from the top of the screen, etc. Manufacturers add an overlay to lock the interface into audio playback functions only. Sometimes, this overlay can be complex, especially when the player has many additional features. You might find you prefer a model with a more straightforward interface.
Wi-Fi
Music players equipped with Wi-Fi are able to connect to the network. This makes it easier to manage the songs stored on the player from a computer. Wi-Fi also offers smartphone-like features, for example, the ability to add apps, such as streaming services like Qobuz. With Wi-Fi, the music player is able to share its internal storage and act as an audio server for other equipment. These additional features aim to maximise its use in different situations.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is widely used on portable music players. Though it’s not recommended for optimum sound quality, it is possible to combine Bluetooth devices with wireless headphones. Most music players are equipped with Bluetooth Hi-Res codecs such as aptX HD and LDAC. This maximises the transmission quality, even if the result is logically inferior to wired headphones. Bluetooth can also be used to transmit music to small wireless speakers, giving the portable music player a dual function: individual listening or music broadcasting.
Battery Life
Battery life is another thing to think about. As portable music players are mobile devices, they run on batteries by necessity. Not all batteries are equal, so the battery life of different music players can differ significantly. Of course, the devices with the best battery life are often the biggest since the battery takes up a considerable amount of space. It’s also useful to remember that playing high-resolution files drains the battery faster than listening to CD-quality files.
Dimensions
Last but not least, consider the dimensions and weight of the music player. As we’ve seen, a large battery is likely to make the device heavier. Some manufacturers create music players with particular designs or opt for thick materials, making them so large that they simply don’t fit in your pocket. Others prioritise ergonomics by making the screen as large as possible, which mechanically increases the size of the player. If you intend to place your music player next to your deck chair out in the garden, size and weight aren’t so vital. However, if you plan to use the player on your way to work or when you’re out for a walk, these features become much more important.
